Study: Mobile Phone Apps to Improve Medication Adherence: A Systematic Stepwise Process to Identify High-Quality Apps
Originally published in JMIR Mhealth and Uhealth (https://mhealth.jmir.org), 02.12.2016
Study Rationale and Background
Medication nonadherence leads to an estimated 125,000 deaths and costs $100 billion annually in the US. There is a vast pool of tools, including medication adherence apps, which are now available to help patients manage their regimens. However, many of these apps available with varying degrees of functionality and health literacy compliance, making it difficult to identify quality apps. The goal of this study is to assess the available applications based on performance.
Methodology
The George Institute for Global Health, University of Sydney study proceeded as follows:
Establish stepwise systematic review with the following steps:
- Search strategy
- Eligibility assessment
- App selection
- Data extraction via predefined set of features considered important
- Analysis by classifying apps through ranking system
- Conducting quality assessment using the Mobile App Rating Scale (MARS)
Selection Process
1471 apps were screened, 1199 apps were excluded for some of the following reasons:
- Not in english
- Not related to health
- Medication list not capable of generating reminders
- Owned by health care services
- Health related but not medication related
Study results
General
- 272 medication reminder apps identified with only 109 free apps
- Median number of features per app was 3.0
- 18 apps had more than nine of the desired 17 features
- Most common features were:
- Flexible scheduling
- Medication tracking history
- Snooze option
- Visual aides
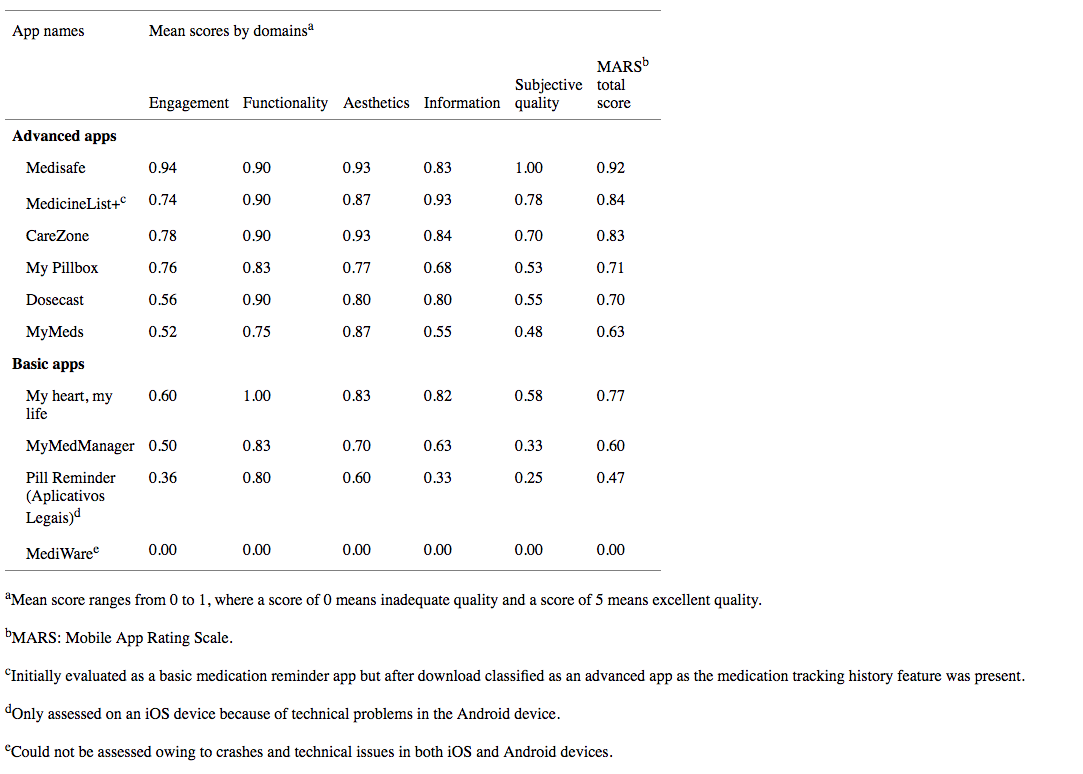
Medisafe
- Medisafe was the highest-scoring app of the 10 apps assessed using MARS and had the highest scores in engagement and aesthetics
- It was found to be interesting, entertaining, highly interactive, and customizable
- Medisafe was the only app rated as having some evidence supporting its effectiveness in nonrandomized studies.
The Mobile App Rating Scale Mean Scores Assessed by Domains
Conclusion and Recommendations
- Should medication adherence apps be proven effective, they can have an impact on clinical practice and other strategies to improve adherence
To see the original study, please click here.
